This is my first post since joining TC Engine, and I want to discuss Smart Legal Contracts. TC Engine, a technology-driven company, focuses on enabling trade compliance for global business. Our team consists of industry experts and thought leaders at the intersection of Global Trade Compliance, Technology, and Product Engineering. We utilize cutting-edge technology like OpenAI, Blockchain, and Azure Cognitive Services to solve practical use cases in our lab for the Defense Industrial Base.
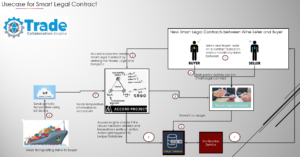
Smart Legal Contracts are generating hype, with many technologists and lawyers collaborating on the topic. Companies have developed tools for authoring and enforcing contracts, such as the Accord Project by Clause, which DocuSign acquired. To understand Smart Legal Contracts, consider a wine merchant with contracts to sell their merchandise to buyers. The signed contract document includes a clause stating that the wine must be maintained below 25 degrees Celsius during shipping until delivery. If the temperature exceeds 25 degrees, the wine spoils and the buyer won’t accept it. Two challenges exist in enforcing this:
- Technical challenge: A temperature sensor in the ship constantly monitors the wine’s temperature.
- Enforcing challenge: Both parties receive notifications if the temperature exceeds 25 degrees Celsius, and the expired item returns to the seller.
Using a diagram, we can examine how this is possible. The ship has a thermostat that sends an alert to a processing engine like Accord when the temperature falls. The engine checks the agreement’s rule, and if it matches, it sends an alert back to the ship. In Smart Legal Contracts, the information is stored as machine-readable rules that can be executed.